Copper is important in supporting renewable energy and electric vehicles (EVs). For example, there’s about 5.5 tons of copper used per megawatt (MW) of photovoltaic generation and there’s 183 pounds of copper in an EV, compared with only 48 pounds in an internal combustion engine (IEC) vehicle. Not all copper is the same; there’s a wide range of copper alloys used in renewable energy and electric (EV) applications.
Copper alloys are made using one or more metals in addition to copper. They offer a range of tradeoffs in terms of conductivity, mechanical strength, and cost. Some applications like the power wiring harness in an EV drive train aren’t subjected to much mechanical stress and benefit from maximum conductivity and minimal cost. On the other hand, slip-ring connectors used in wind turbines must be able to withstand challenging mechanical conditions. Not surprisingly, those two applications use different copper alloys.
Conductivity vs tensile strength
In addition to cost, conductivity and tensile strength are basic parameters for wires, and other connectivity elements. The International Annealed Copper Standard (IACS) was developed by the International Electrochemical Commission. The conductivity of the annealed copper is 5.8001 x 107 Siemens per meter (S/m) and is defined as 100% IACS at 20 °C.
Tensile strength is the maximum amount of axial stress that a material can take before breaking. Strength measurements can be made in ksi (kilo-pounds per square inch). The weight a wire can withstand can be determined by multiplying ksi by the area of the cross-section of the wire.
Electrolytic Copper
Electrolytic copper has been refined using electrolysis. This type of refined copper can be over 99.9% pure. Many metals can be added to copper to adjust the tradeoff between cost, conductivity, and strength. Figure 1 shows how some metals can be added to increase the strength of copper but with a corresponding reduction in conductivity.
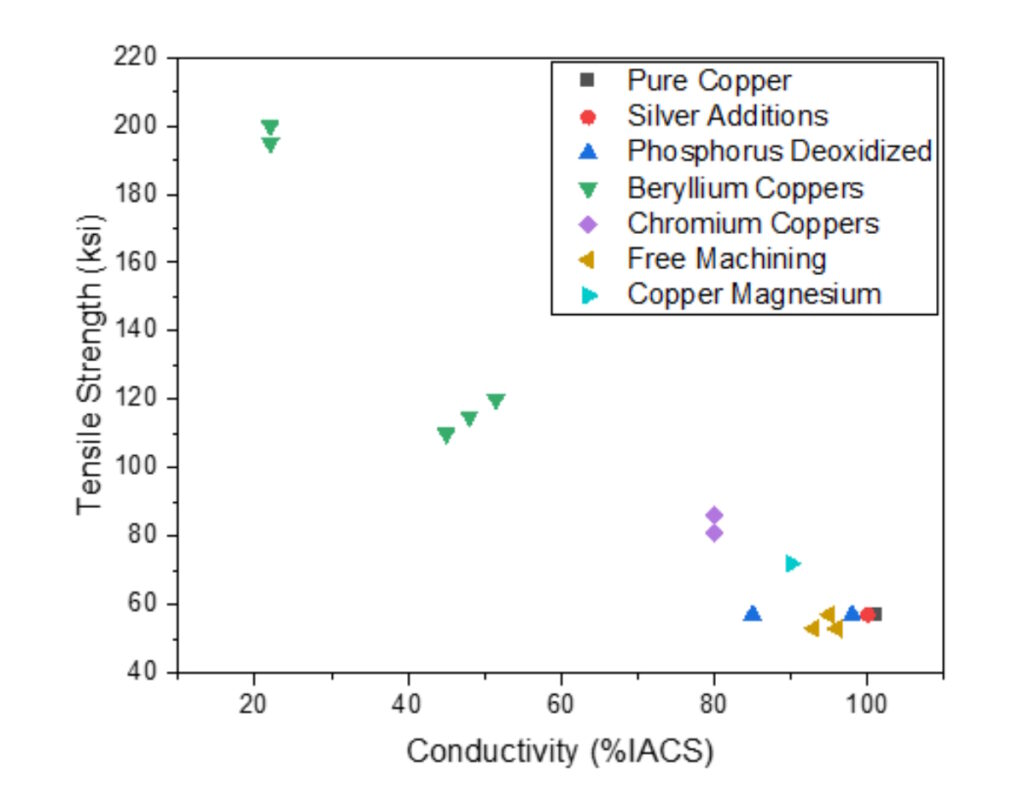
Copper alloys for connectors
There are several copper alloys that are especially suited for use in connectors. Copper-zinc (brass) has great electrical properties but low yield strength. It’s not generally used for contacts, especially for connectors that must withstand more than a very few mating/unmating cycles. It’s sometimes used in parts of connectors that are not subject to high mechanical demands, like weld tabs.
Beryllium copper can provide the optimal combination of strength and conductivity, but it’s relatively expensive. It’s used in micro connectors and in demanding high-cycle applications.
Bronze consists of copper with about 12% tin. Adding phosphor results in phosphor bronze, that’s stronger than brass but not as good as beryllium copper. While beryllium copper is good for microcontact systems, phosphor bronze is used for larger contact systems.
Copper-nickel-tin with about 9% nickel by weight and 2% tin by weight is another common copper alloy used in connectors. Its excellent relaxation properties make it highly suitable for fabricating contacts. Other properties that make it suitable for connectors are its high corrosion resistance, good solderability and high temperature stability.
Copper nickel silicon for wind turbines
Copper nickel silicon combines very high strength with excellent wear and corrosion resistance, plus good electrical and thermal performance. Its high strength makes it particularly useful for current-carrying applications like slip rings in wind turbines, industrial squirrel cage motors, short-circuit rings, and heavy-duty switchgear (Figure 2).

Other qualities that make it especially use for applications like slip rings include high galling resistance, good electrical and thermal conductivity, very low magnetic permeability, excellent corrosion resistance and very good low-temperature mechanical characteristics. In addition, it has good machinability and dimensional stability.
Summary
There is no single “best” copper alloy. There’s a wide range of alloys that offer various combinations of costs, conductivity, and mechanical strength. There are several copper alloys especially suited for connectors in electronic systems and applications like EVs. Other alloys provide a better combination of mechanical strength and stability along with electrical and thermal conductivity that makes them suited for rotating applications like slip rings in wind turbines.
References
Comparing Base Metals In Connectors, Samtec
Copper in Electric Vehicles, Copper Development Association
Copper Nickel Silicon, Metelec
Electrolytic Copper, Wire Association International
Harnessing the Power of Wind: Slip Ring Connector, Grand Slipring
High Copper Alloys for Electrical Contact Assemblies, Deringer-Ney


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.