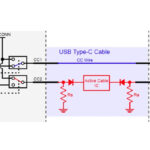
USB4 represents a significant change from past standards from the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF). It is based on the Thunderbolt 3 protocol. Support of Thunderbolt 3 interoperability is required on all ports for USB4 docks, for downward-facing ports on hubs, and is optional for USB4 hosts and peripheral devices. Like Thunderbolt, USB4 allows tunneling of […]
A guide to USB standards from 1.0 to USB4
The evolution of USB standards has been instrumental in shaping the landscape of modern computing and connectivity. From the basic functionality of USB 1.0 to the enhanced capabilities of USB4, each iteration has brought significant improvements in data transfer speeds, power delivery, and device compatibility. As a result of USB’s rapid advancement, the constantly changing […]
How does OPC UA PubSub data support connector digital twins?
The use of digital twins can be an important factor in maximizing the performance and flexibility of Industry 4.0 factories. Open Platform Communications (OPC) is the interoperability standard for the secure and reliable exchange of data in industrial automation environments. OPC has been expanded to include the unified architecture (UA), standardized as IEC 62541, that […]
How do connectors made with conductive plastics contribute to sustainability?
Basic plastics are electrically insulating, but with the proper additives, they can become conductive. Electrically conductive plastics can be used to replace metal components and improve sustainability in several areas of connector construction. They take less energy to fabricate and are lighter, reducing system weight, a very important consideration in applications like electric vehicles (EVs). […]
How does UCIe on chiplets enable optical interconnects in data centers?
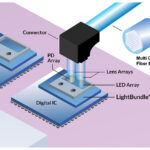
Chiplets enable heterogeneous integration of various process nodes and materials to maximize performance. UCIe is a new die-to-die interconnect standard for high-bandwidth, low-latency, power-efficient, and cost-effective connectivity between chiplets. UCIe is also the first specification to include an interface that is compatible with optical links. Large computing systems needed to support high-performance computing (HPC) applications […]
What is the best copper alloy for connectors in renewable energy and EV applications?
Copper is important in supporting renewable energy and electric vehicles (EVs). For example, there’s about 5.5 tons of copper used per megawatt (MW) of photovoltaic generation and there’s 183 pounds of copper in an EV, compared with only 48 pounds in an internal combustion engine (IEC) vehicle. Not all copper is the same; there’s a […]
How can carbon nanotubes improve interconnect performance?
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been proposed for reducing fretting wear in connectors used in high-vibration environments like vehicles. They can also be used to make contacts with lower contact resistance and higher corrosion resistance compared with silver (Ag) plating, and they have been used to reduce the weight in some shielded cables by 25% or […]
What are ZIF and LIF connectors and where are they used?
How low contact resistance is achieved can be a key differentiator between zero insertion force (ZIF) and low insertion force (LIF) connectors. Many LIF connectors have a low contact resistance of about 30 mΩ when mated without needing a locking mechanism. ZIF connectors generally require a locking mechanism to achieve low contact resistance and a […]
What are the four MICE elements and three performance levels for connectors?
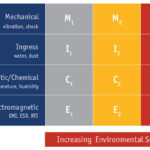
IEC 11801-3:2017 provides guidance for designing physical infrastructure to support network communications in a manufacturing environment. That guidance is in the form of four MICE elements and three performance levels. The four elements of the MICE acronym include Mechanical, Ingress, Chemical/climatic, and Electromagnetic compatibility. The MICE standards define three performance levels and apply to cabling […]
How do the three types of shielded cables work?
The three basic types of shielding for electromagnetic interference (EMI) in cables include strands of braided copper and similar metals, spiral shields, and foil or tape shields. They can be used separately or in combination. This FAQ begins with a review of the three types of shielding, then considers how they are used in combinations […]