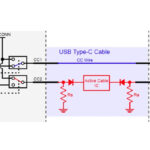
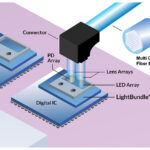
Past and current data center hardware systems developers occasionally require and evaluate unexpected or previously unimagined connectivity solutions. These novel solutions often require a very short development cycle and low cost of ownership targets. Leading-edge test and measurement equipment developers sometimes need a good fast solution as a bridge product before qualifying a new connector […]
Featured
How mmWaves affect cables, connectors, and PCB traces
Millimeter-wave signals used in 5G networks provide wide bandwidth and high data rates. Signal losses, both over the air and through interconnects, bring design challenges. by Ketan Thakkar, Cinch Connectivity Millimeter wave (mmWave) signals offer engineers countless application possibilities, including ranging, object detection, and mapping. Unfortunately, mmWaves bring numerous design challenges. Not only do mmWave […]
USB proliferation of capabilities and compatibilities
USB4 represents a significant change from past standards from the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF). It is based on the Thunderbolt 3 protocol. Support of Thunderbolt 3 interoperability is required on all ports for USB4 docks, for downward-facing ports on hubs, and is optional for USB4 hosts and peripheral devices. Like Thunderbolt, USB4 allows tunneling of […]
How does OPC UA PubSub data support connector digital twins?
The use of digital twins can be an important factor in maximizing the performance and flexibility of Industry 4.0 factories. Open Platform Communications (OPC) is the interoperability standard for the secure and reliable exchange of data in industrial automation environments. OPC has been expanded to include the unified architecture (UA), standardized as IEC 62541, that […]
How do connectors made with conductive plastics contribute to sustainability?
Basic plastics are electrically insulating, but with the proper additives, they can become conductive. Electrically conductive plastics can be used to replace metal components and improve sustainability in several areas of connector construction. They take less energy to fabricate and are lighter, reducing system weight, a very important consideration in applications like electric vehicles (EVs). […]
How does UCIe on chiplets enable optical interconnects in data centers?
Chiplets enable heterogeneous integration of various process nodes and materials to maximize performance. UCIe is a new die-to-die interconnect standard for high-bandwidth, low-latency, power-efficient, and cost-effective connectivity between chiplets. UCIe is also the first specification to include an interface that is compatible with optical links. Large computing systems needed to support high-performance computing (HPC) applications […]
What are the key design and selection considerations for MIL-SPEC connectors?
MIL-SPEC connectors are designed to operate reliably in challenging conditions and extreme environments. First developed in the 1930s for the US Armed Forces, military standard connectors are now used across multiple industries, from energy and aerospace to maritime and automotive. This article discusses key MIL-SPEC connector design requirements and reviews crucial connector selection criteria. It […]
What is the best copper alloy for connectors in renewable energy and EV applications?
Copper is important in supporting renewable energy and electric vehicles (EVs). For example, there’s about 5.5 tons of copper used per megawatt (MW) of photovoltaic generation and there’s 183 pounds of copper in an EV, compared with only 48 pounds in an internal combustion engine (IEC) vehicle. Not all copper is the same; there’s a […]
How can carbon nanotubes improve interconnect performance?
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been proposed for reducing fretting wear in connectors used in high-vibration environments like vehicles. They can also be used to make contacts with lower contact resistance and higher corrosion resistance compared with silver (Ag) plating, and they have been used to reduce the weight in some shielded cables by 25% or […]
What are ZIF and LIF connectors and where are they used?
How low contact resistance is achieved can be a key differentiator between zero insertion force (ZIF) and low insertion force (LIF) connectors. Many LIF connectors have a low contact resistance of about 30 mΩ when mated without needing a locking mechanism. ZIF connectors generally require a locking mechanism to achieve low contact resistance and a […]