There are numerous standards for heavy-duty connectors (HDCs) and general industrial connectors. An HDC is defined as a rectangular connector that can handle power, data, and signal pins in a single housing and is designed for use in challenging industrial and transportation environments. They are a subset of general industrial connectors.
This FAQ does not review UL 1977 or IEC 61984, which are widely used general connector standards that are required in some industrial applications. This discussion provides an overview of a few standards specific to industrial environments and looks at connector size standards and power wiring color coding standards.
UL 2237 & 2238 are both industrial connector standards with UL 2237, including the primary requirements of UL 2238, but with some additional testing for power transmission safety. For example, in UL 2237, there is no current limit, and the voltage limit is 1 kV AC or DC. In addition, UL 2237 requires a short circuit current raging and must meet a 5-kA minimum rating that is optional for UL 2238. The cumulative impact of the differences between the two standards is the final current rating that connectors can achieve. For example, 7/8-inch form-factor cord sets and connectors can often achieve a current rating of 25 A under UL 2238, but when the same connector is retested to the UL 2237 standards, the current rating can drop to 15 A. That makes the 7/8-inch designs uncompetitive with smaller M12 cord sets and connectors that can achieve a 16 A rating under UL 2237.
SAE J2030 Heavy-Duty Electrical Connector Performance Standard covers connectors between two cables or between a cable and an electronic device. It’s focused on DC power systems rated for 50 Vdc or less, like those found in off-highway machinery. Tests include detailed procedures and performance requirements for:
- Electrical
- Low-level contact resistance (dry circuit)
- Contact resistance (voltage drop)
- Mechanical
- Crimp tensile
- Contact retention
- Durability
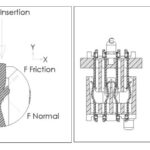
- Terminal-terminal insertion force
- Contact overlap (electrical engagement)
- Environmental
- Temperature life
- Thermal cycles
- Thermal shock
Connector sizes
Rectangular HDC connectors are available in a range of standard sizes, from small 3A devices to large 32B designs. The size of these connectors is based on the distance between the center points of the four installation screws. Those four installation screw locations are found on both the insert and housing. Table 1 shows where the X-Y distances are measured and delineates the related HDC sizes.

M-style circular connector sizes are based on the size of the metric thread on the coupling nuts and receptacles. Common sizes are M5 (5 mm), M8 (8 mm), and M12 (12 mm). There are also subcategories based on keying and application, including:
A – for sensors, dc power, and 1 Gigabit Ethernet.
B – for Fieldbus and Profibus.
C – for ac power for sensors and actuators.
D – for 100 Megabit Ethernet and Profinet.
X – for 10 Gigabit Ethernet and power over Ethernet (PoE).
S – for ac power.
T – for dc power.
Color-coded connectors
Power connectors for single-phase power and three-phase motors, generators, wind turbines, and power distribution boards are required to be color-coded. These connectors can be rated for 600 A and higher, and the color coding varies by geographic region (Figure 1).

Summary
There are several important standards for heavy-duty and general industrial connectors. Those standards cover electrical, mechanical, and environmental performance requirements. In addition, there are standards defining HDC and M-series connector sizes and regional standards for color coding single- and three-phase power connections.
References
An Easy Roadmap to Understanding Connector Certification Levels, UL
Heavy-Duty Electrical Connector Performance Standard J2030, SAE International
The Basics of Circular Connectors and Cables, CUI Devices


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.